(2015) Sensor-Based Worker Monitoring
Explore the use of wearable sensors for monitoring worker physiological status and activities both at work and off duty as a part of the Total Worker Health study.
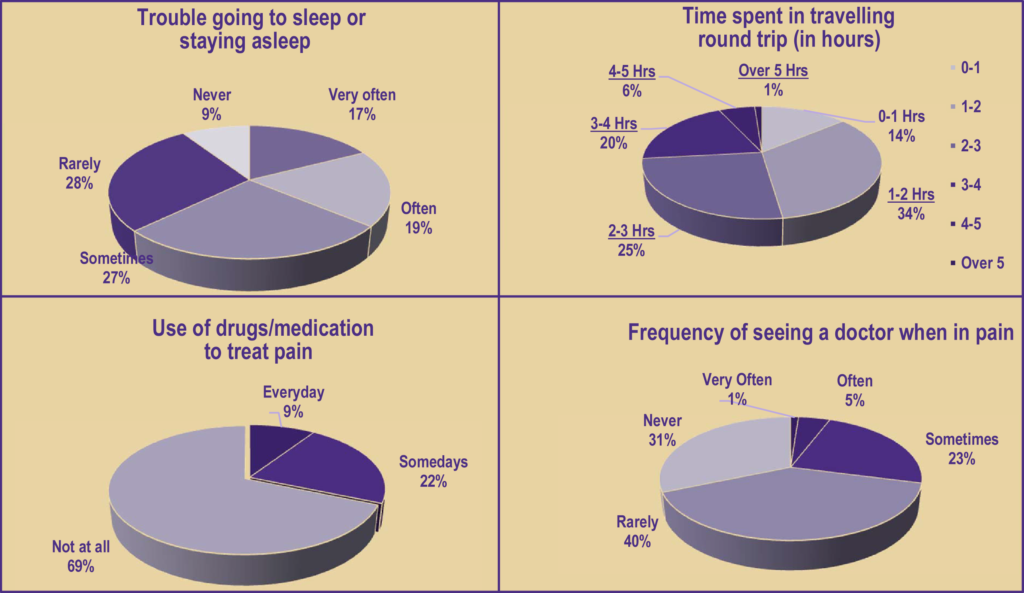
Total Worker Health® (TWH) integrates occupational health and safety with the promotion of workers’ off-duty wellbeing. Wearable sensors (e.g., activity trackers and physiological monitors) have facilitated personalized objective measurement of workers’ health and wellbeing. Furthermore, the TWH concept is relevant to construction workers, especially roofing workers, as they encounter high on-duty health and safety risks and have poor off-duty lifestyles. This study examined the reliability and usability of wearable sensors for monitoring roofing workers’ on-duty and off-duty activities. The results demonstrated the usability of these sensors and recommended a data collection period of three consecutive days for obtaining an intraclass correlation coefficient of ≥ 0.75 for heart rate, energy expenditure, metabolic equivalents, and sleep efficiency. The participants exhibited significant variations in their physical responses, health statuses, and safety behaviors. Moreover, several issues were identified in the application of wearable sensors to TWH evaluations for construction workers including roofers.
Related Publication:
Lee, W., Migliaccio, G., Lin, K.Y. and Seto, E. (first published online on Dec. 24, 2019) “Workforce Development: Understanding Task-level Job Demands-Resources, Burnout, and Performance in Unskilled Construction Workers”, Safety Science, Vol. 123, Mar. 2020, 104577.
Lee, W., Lin, J.H., Bao, S., and Lin, K.Y., (2019) “Validity and Reliability of a Posture Matching Method Using Inertial Measurement Unit-based Motion Tracking System for Construction Jobs”, in the proceedings of the 2019 ASCE International Conference on Computing in Civil Engineering, Jun. 17 – 10, 2019, Atlanta, Georgia.
Lee, W., Lin, K.Y., Seto, E., and Migliaccio, G., (Nov. 2017; first published online on June 21, 2017) “Wearable Sensors for Monitoring On-Duty and Off-Duty Worker Physiological Status and Activities in Construction”, Automation in Construction, Vol. 83, 2017, pp.341-353.
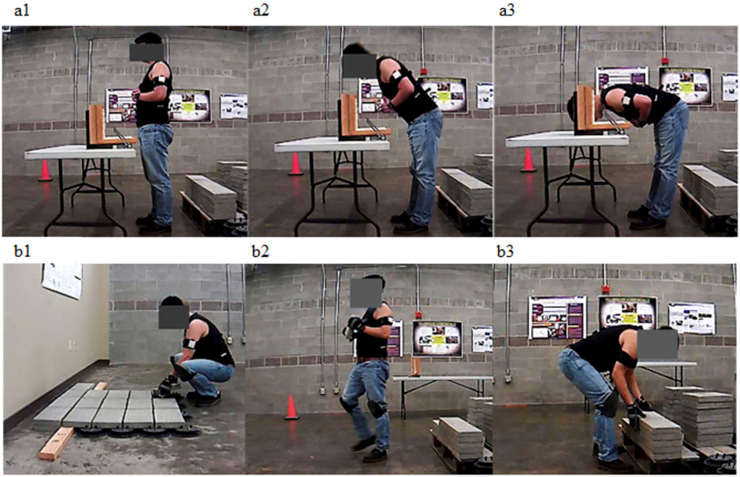
Lee, W., Seto, E., Lin, K.Y., Migliaccio, G. (Nov. 2017; first available online on April 15, 2017) “An Evaluation of Wearable Sensors and Their Placements for Analyzing Construction Worker’s Trunk Posture in Laboratory Conditions”, Applied Ergonomics, Vol. 65, pp. 424 – 436.
Lee, W., Lin, K.Y., Migliaccio, M., and Seto, E., (2016) “Comparison of Alternative Wearable Accelerometers to Analyze Construction Workers’ Ergonomic Posture in Laboratory Conditions”, Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering (ICCCBE) 2016, July 6 – 8, 2016, Osaka, Japan.
Lee, W., Migliaccio, M., and Lin, K.Y. (2015), “Lessons Learned From Using Bio- And Environmental Sensing In Construction: A Field Implementation”, Proceedings of the 2015 International Construction Specialty Conference, June 7 – 10, 2015, Vancouver, BC, Canada.